
Figure 4.1
1) Minimum Requirements
2) Recommended Requirements
3) How to calculate the hard disk and memory space WFilter needed?
| Componment Name | Describe | Default Install Directory |
|---|---|---|
| WFilter_trial.exe | Main installation package. Installed list: 1. Service: WFilterd. 2. Process: startsys.exe,webservd.exe. |
C:\Program Files\IMFirewall\WFilter |
WFilter can be installed on a single Windows machine for a small network. WFilter supports TCP/IP-based networks only. If your network uses both TCP/IP and non-TCP protocols, only those users on the TCP/IP portion of your network will be filtered.
Network Considerations
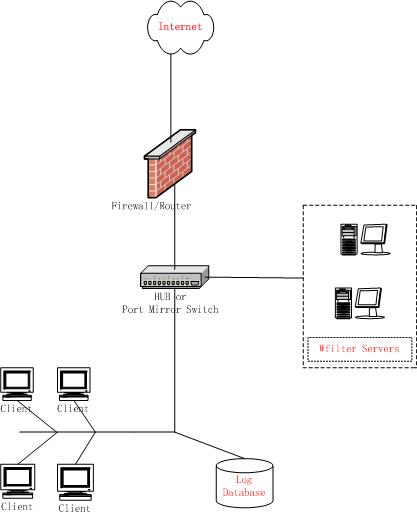
Figure 4.1 provides a synopsis of small network deployment. You only need to install WFilter at a single location where it can monitor all Internet traffic of the internal network.

In a medium network(500-2500 users), WFilter should be distributed on two or more dedicated machines, depending on your operating environment. These dedicated machines can use a central database for data storage. We recommend one dedicated machine monitor no more than 500 computers.
Network Considerations
Figure 4.2 provides a synopsis of medium network deployment. All dedicataed machines of WFilter use a same network database.
In a large network(2500+ Users), WFilter should be distributed on two or more dedicated machines, depending on your operating environment. The deployment on dedicated machines is the same as a medium network deployment.
Distributed enterprises are corporations with large numbers of remote locations, ranging from dozens to thousands of small offices. Some of these organizations use a decentralized network topology that provides each remote office with its own Internet connection.WFilter Enterprise can be deployed regionally and communicating over the Internet. Or you can install WFilter in each office separately. You also can apply uniform filtering policies to hundreds of remote offices from a central location.
Network Considerations
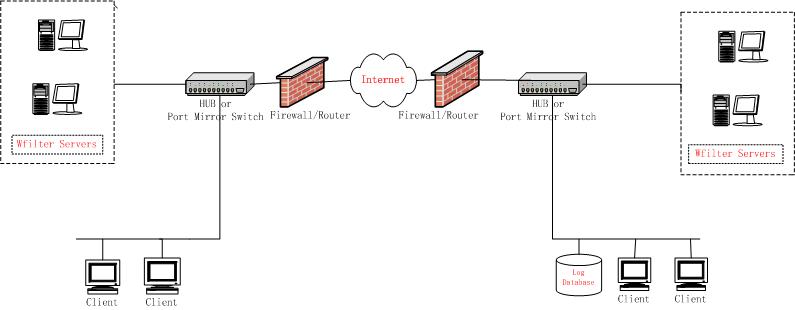
Figure 4.3 provides a synopsis of large network deployment. Several dedicataed machines of WFilter use a same network database.
A single segment network is a logically connected nodes operating in the same portion of the network. These nodes can be PCs, printers, other networked devices. In a such a network, WFilters must be installed where they can monitor Internet traffic across the entire network. You shall set the monitor mode to "by MAC address" in "Monitoring Settings".
Below are some typical network environments:
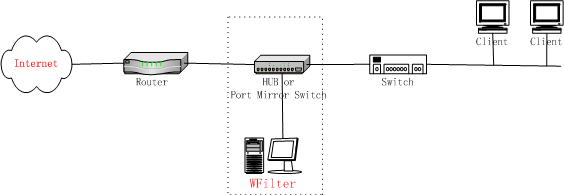
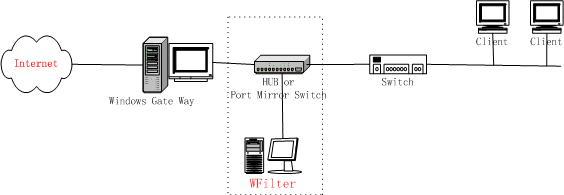
As in Figure5.1.1,local computers use a wireness router to connect to the Internet.Under this type network, it requires a broadcasted hub or a port mirroring switch between gateway and switch.And the machine with WFilter installed shall connect to the hub or the monitor port of the port mirroring switch.
As most broadcasted hub only works in 10Mb speed,we recommend you use a port mirroring switch if your internet bandwidth larger than 4Mb.
Recommended hub: TPLINK's TL-HP5MU, recommended port mirroring switch: TPLINK's TL-SF2005.
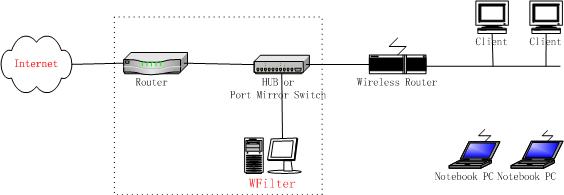
You may monitor your wireless lan by sniffing on your wireless card directly. If your network use both wireless network and wireness network.You need to add a wireness router and a broadcasted hub(or port mirroring switch).
Network Topology:
If your gateway runs a windows system(Windows2000,Windows XP,Windows2003 Server),you may install WFilter on this computer to monitor the whole network.
If you prefer not to install the software on gateway or your gateway is running Linux. You can insert a broadcasted hub between the switch and gateway, or create a port mirror on the switch.
Network Topology:
Depending on the device connecting multiple network segments, some traffic may not be sent to all segments. A router, bridge or smart hub may serve as traffic control, preventing unneeded traffic from being sent to a segment. In such a situation,we can not use "by MAC address" mode because a MAC address will related to more than one computer.
We have two solutions for you:
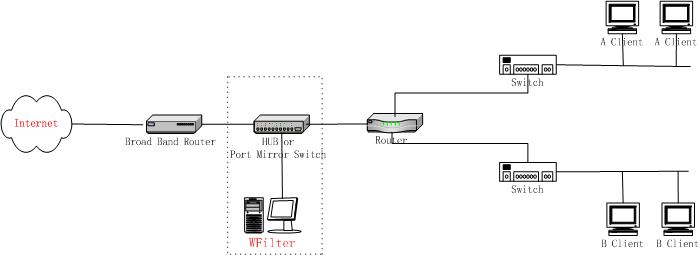
You can put WFilter at a single location and use "by IP address" mode.But this will cause some trouble if your users change their IP address rapidly.We suggest you use "IP-MAC binding" to avoid unauthorized change of IP address.
As in Figure 5.2.1, it requires a broadcasted hub or a port mirroring switch between gateway and switch.And the machine with WFilter installed shall connect to the hub or the monitor port of the port mirroring switch.You also need to set monitor mode to "by IP address".
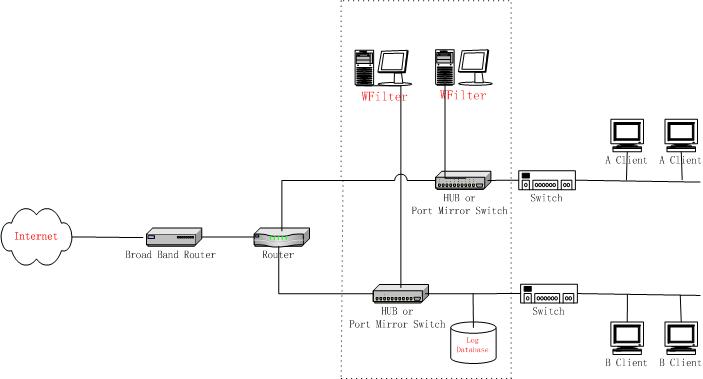
The second solution is deploying WFilter in each network segment.And all the dedicataed machines of WFilter use a same network database.
Basically,a computer connected to a switch or a route can only receive its own traffic.To monitor other computers,your machine shall be able to monitor other computer's Internet traffic.
A broadcasted hub is a data packet repeater commonly used in broadcast networks. In a broadcast network, a node will send a packet that traverses through every other node until the recipient accepts the packet. Every node in the network will conceivably receive this packet of data until the recipient processes the packet. In a broadcast network, all packets are sent in this manner.So each computer connected to a broadcasted hub can monitor other computers.(Recommended Hub: tplink's TL-HP5MU)
In a switched network, packets are not broadcasted, but are processed in the switched hub which, in turn, will create a direct connection between the sending and recipient nodes using the unicast transmission principles. This eliminates the need to broadcast packets to each node, thus lowering traffic overhead.
The advent of switched networks resulted in Network IDS having great difficulty in promiscuously monitoring their networks. This was overcome by configuring a switch to replicate the data from all ports or VLAN's onto a single port. This function has a multitude of names including: Port Mirroring, Monitoring Port, Spanning Port, SPAN port and Link Mode port.
Generally Port Mirroring usually indicates the ability to copy the traffic from a single port to a mirror port but disallows any type of bidirectional traffic on the port.
Spanning Port usually indicates the ability to copy traffic from all the ports to a single port but also typically disallows bidirectional traffic on the port. In the case of Cisco, SPAN stands for Switch Port ANalyzer.
Some switches do not allow SPAN ports to transmit packets, this is an issue if you wish to use WFilter block features.
As described above,to monitor all Internet traffic,should consider two conditions:
A broadcasted hub is a data packet repeater commonly used in broadcast networks.
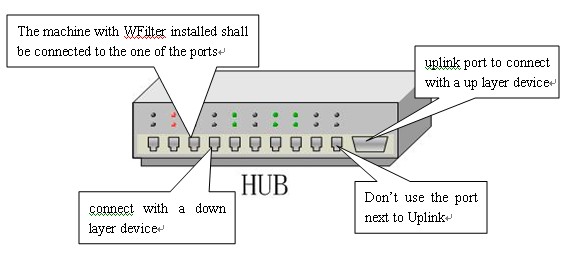
Most broadcasted hubs provide a uplink port to connect with a up layer device.You shall connect the up layer device to the uplink port of the hub(Note: Do not use the nearby port with the uplink).
As in Figure6.2:
Most broadcasted hubs only work in 10Mb speed,and all the computers connected to the hub will share the bandwidth. For example, if two computer connected, each will have 5Mb bandwidth.So we recommend you use a port mirroring switch if your internet bandwidth larger than 4Mb.
The machine with WFilter installed shall be connected to the mirror port of a switch.As in Figure6.3.
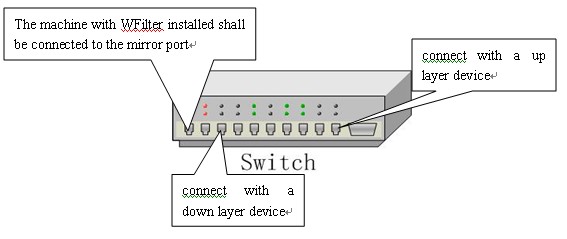
Different switch provide different configuration.Below we provide some common switchs' port mirroring configuration.
How to use "Huawei Lanswitch View" management system to add a mirror port:
In 3COM switch,port mirroring is named as "Roving Analysis".The port been mirrored is called as "Monitor Port", The mirror port is called as "Analyzer Port".Configuration commands:
Define an analyzer portCISCO CATALYST has two series. The mirror port is named as "analysis port".
1. Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950(CLI based)